Contact us.
www.blockmaterials.com
info@blockmaterials.com
31(0)6 269 028 26
VISITING ADDRESS
C-mill – building 5
Jan Campertstraat 5
6416SG Heerlen
The only way to preserve our resources and not further deplete the world is to create a revenue model.
This is what Block Materials does for the real estate world in which we assign property rights to organize the social value and marketability of materials.


CFO and founder of Blockmaterials

Architect and Founder of Blockmaterials
As an architect and founder of Blockmaterials, I am constantly trying to organise chaos and create new values. Every situation offers an opportunity to translate the past into solutions for the future. My organisation enables me to propagate this vision, tackling projects and processes within and outside the region, where the problem definition is often complex. My strength lies in quickly understanding the dynamics within a situation and translating them into concrete, solution-oriented actions.
My creative mind and expertise allow me to develop ideas into market-ready products. In a changing society, where the role of each player in the demolition and construction process needs to be redefined, I see unlimited opportunity for innovation. This requires different thinking and working processes.

Architect & Project Lead Manager
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
The Circular and modular homes for social housing project aims to realize a market-
ready, economically feasible, circular, flexible and attractive solution to the challenges
in social housing through regional chain collaboration.
The basis of the new living concept is to make the modular circular terraced house
suitable for social housing. The house is distinguished by the fact that it: (1) can be
dismantled, so that its materials can be recovered and reused after use; (2) is built
with sustainable (biobased (roadside grass) and circular) materials; (3) is built using a
nitrogen-free modular construction method; (4) is affordable and low-maintenance;
(5) has a long lifespan and is suitable for temporary and permanent housing; (6) is
comfortable, attractive and quickly available; and (7) is energy efficient and self-
sufficient (NOM home energy-saving windows and insulation.
In order to make an impact, it is important to work multidisciplinary and with the entire
chain and to respond to the wishes of the end users.
For this purpose, the consortium formed, led by the Brightlands Chemelot Campus,
consists of various chain partners, from (SME) businesses to knowledge institutions,
from technology developers to housing associations and from training centers to
market parties. In addition, resident panels/starters are involved in this project
through a housing association, open innovation is used to deploy circular innovations
from Limburg SMEs and startups in the demonstration homes, and there are experts
such as Rabobank in the field of financing (see partner description and LOI (
Appendix A)) involved in relevant issues such as the financing model and scaling up.
The Chemelot Campus supports the developers in the development and testing of
the new materials and manages the project.
Block Materials, in collaboration with the Maeconomy Foundation, is the hub in the
web for developing the living concept. In particular on the revenue model of the
concept. This revenue model guarantees circular use of materials. Materials retain
value, meaning they can be taken back by manufacturers after use and reused for
the same applications. Retaining value means lower costs for the user.
To make the home even more financially accessible, an accessible method of
financing is being sought. The combination of a circular revenue model and
accessible financing model makes the high quality of the circular home available for a
low price.
The Consortium consists of Chemelot Campus, CHILL, CUBE Homes, Stichting
Maeconomy, ECOR, Mosa Tiles, TNO/BMC, Bouwmensen, Zuyd Hogeschool,
ZOwonen, Rabobank. The project is subsidized in part by the European Union’s OPZuid grant.


The intense use of raw materials in the construction sector, which represents more than 40% of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions when accounting for the first use of materials, is jeopardized by their scarcity, economic value, and environmental footprint. Urban mining, consisting in the reclamation of materials and elements from any kind of anthropogenic stocks, including buildings or infrastructures, can be articulated as an alternative to depleting natural resources. As the decarbonisation of all sectors is needed to achieve a carbon neutral EU by 2050.
Also, the intermediate GHG emission reduction target for 2030 is set at 55%4, circularity is broadly supportive of sustainability and may be seen as one of the conditions and main solutions for transformation to a sustainable built environment. Construction and demolition waste (CDW) excluding mining wastes represents the largest waste stream in the EU in terms of mass.
Based on Eurostat data, CDW generation is growing. In 2020, the total amount of CDW produced in EU27 was 330 Mt (excluding excavated soil, dredging spoils). This number covers waste generated during the different building phases (construction, renovation, and demolition), out of which the demolition phase is dominating. Although the recovery rate of CDW in EU is high, the waste is mainly used in low-grade applications like earth construction.
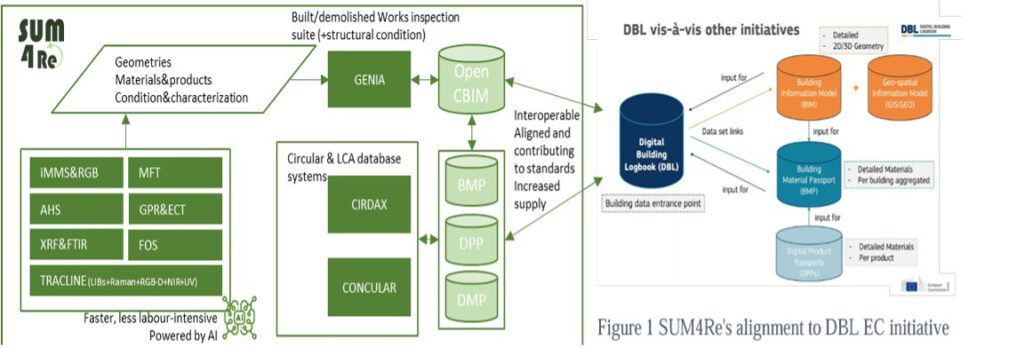
To overcome the different obstacles to circularity that emerge from stakeholders in the value chain, a special focus must be put on making relevant data for decision-making easily available to new and upcoming standardized digital instruments, such as Waste Audits, Digital Material Passports, Digital Product Passports, Digital Building Logbooks or EU Construction and Demolition Waste Management Protocols.
Aligned to the EU DBL initiative (Figure 1), SUM4Re aims to deliver an integral approach to create materials banks from the built environment by combining urban mining and technologies for automated data acquisition ([1] identification) and modelling ([2] analysis). A paradigm shift from conventional BIM towards an open circular guided BIM is proposed to support new business models on secondary materials and therefore to [3] realise circularity. The actual contributions of SUM4Re will be a set of measurable results that will be implemented and validated through 15 Use Cases (UC).

Disclaimer
Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the
author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or [name of the
granting authority]. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held
responsible for them.
Based on its work in projects and for the Regional Government, Block Materials designs initial notes, business cases and further applications of Circular Craft Centers in municipalities. These Craft Centers are among the national spearheads of a Circular Economy and also receive finances from the government for implementation and daily operational matters. If you would like to get started with a Circular Craft Center, please contact us.
Block Materials has carried out a number of studies for the Parkstad Limburg Region for the further development of the Regional Circular Economy. The three documents she produced: a. “Building blocks for Circular Construction and Demolition”, b. “Transformation of the Built Environment and Circular Demolition” and c. Implementation of Digital Deconstruction in Parkstad Limburg will set up the development of a Circular Construction and Demolition Implementation Program in a Region. This blueprint for the Parkstad Limburg region can be applied in the same way in several regions.
Any material that is reused no longer needs to be produced. This also means that CO2 during the production of a material is prevented through this reuse. Block Materials has developed a module within the Cirdax application that makes various environmental calculations. Including the CO2 saved as a result of using secondary materials. The Co2 module uses the data of materials in a building as a basis for the calculations. For the “embodied Co2” per material, the University of Bath’s ICE database is the central starting point. The calculation options with the Co2 module are expanded to a wider range of desired indicators, such as MKI, MPG, or elements from Breeam, Gro, Level(s) and Totem for the Belgian market. Partly to support specific target groups, such as architects.
Block Materials unites the application of blockchain technology with materials in a building. Based on an inventory of materials in a building, Block Materials adds a property right to the material passport of a material based on the #hash. A right of ownership that can also be checked through verification using blockchain technology, thus guaranteeing this right of ownership. Based on this ownership right per material, this material can then be traded, the ownership of the material can be tracked over time, it is possible to enforce liability for future delivery, or the ownership right can be linked to other rights, such as emission rights on the production or reuse of materials. Blockchain technology replaces the role of notaries and appraisers in this regard and results in completely different transaction costs on materials than were previously the case. Block Materials studies all costs and benefits that come to light as a result of this innovation in the various projects in which it works.
Knowledge of the Circular Demolition Process is one of the building blocks of a local circular economy. In the context of the Sustainable Innovation Scheme of Parkstad Limburg and the Digital Deconstruction project, Block Materials has developed a Circular Demolition Handbook that can also be consulted via this link. The manual takes the daily practice of a real estate owner as a starting point, with the central question being classic or sustainable demolition. The manual presents the process of sustainable demolition using 12 steps. The decision to demolish conventionally or sustainably is central, with one half of the manual focusing on the preparation of this decision, and the other half continuing with the decision to demolish sustainably and what to do next. The book works with the central methodology of Blockmaterials in which the trade-off between more value from materials versus carrying out inventories, repairs, refurbishment, etc. follows the common thread. The book contains many practical examples, tools and suggestions on how to tackle sustainable demolition. She does this for each step in the described process.
On the demolition portal you can find all products that are made for companies and organizations that (want to) get started with Circular Construction and Demolition. This concerns access to our instruments, such as Cirdax and the various Manuals, as well as Education modules for the Demolition Industry. Via the Demolition Portal you also have access to the Sustainable Demolition Calculation Tool, with which you can calculate in advance whether making a material inventory is effective for you. Based on a number of characteristics of a building, she calculates the additional costs of sustainable demolition, and also immediately indicates what the additional revenues are, because the value of the inventoried materials increases due to the work. You can also order an inventory afterwards. You can access the Demolition Portal here.
Data about buildings and materials are an important basis for a different construction process. In the OP-Zuyd project Circular and Modular Homes for Social Housing, Block Materials provides building and material passports for the desired demonstration homes. Based on these passports and the ownership rights to parts of the home, we investigate alternative forms of financing the building, the parts of the building, as well as the size and method of financing by the (future) owner of this home. In this way we contribute to the combination of efficient use of materials, efficient financing and affordable housing. The program runs from 2023 to 2026.
In the European research program CircularB (part of the COST network), Block Materials investigates how a holistic and integrated analysis of the reuse of materials in buildings can be given shape. Block Materials provides the project with both legal and economic foundations for this challenge, as well as educational models in which employees can be trained in the future. The program runs from 2022 to 2026.
The Circular Hubs project investigates the redesign of logistics flows of construction waste in the Parkstad Limburg region as a result of higher values of secondary construction materials in economic traffic. After all, if materials have become more valuable through inventory, repair and/or refurbishment, they can be sold in a different way than is currently the case. This requires research into the retail structure of such materials, or a different organization of the sorting, cleaning and processing process. Block Materials is collaborating with Bouwkringloop and Rd4 on this project. The project also serves as assistance for the Circular Craft Places project.
Block Materials is working in the European Demo-Blog project in collaboration with partners ReUseMaterials, VITO and Leap Forward on an Interactive Marketplace for Architects in Belgium. After all, if verified secondary materials, as made visible with the help of the Cirdax database and blockchain registrations, also find their way into new applications, these materials must be on the radar of architects, project developers and construction companies that use them. wish to use materials. For the latter, the availability and quality of the materials must be transparent for both suppliers and buyers of materials. Both sides of the transaction of secondary materials will also have to match each other, so that payment, logistics, as well as repair and refurbishment of the materials can be organized. The project runs from 2022 to 2026. Block Materials wants to put the project on the market in a first version in 2024.

The core of the instruments that Block Materials develops lies in the possibility of reducing information differences (market failure) about the quality and availability of materials in buildings for the purpose of connecting supply and demand in circular processes. This application of George Akerlof’s The Theory of Lemons to the world of buildings not only requires the large-scale availability of Building Passports for innovation in construction, but also shows that Building Passports cannot simply be created. They form a so-called Collective Good, for which government intervention in the financing of such a “digital highway” is desirable. Block Materials is working within the European Center for Circular Construction and Transformation consortium on the financing of this National Infrastructure by compiling an application for it with the National Growth Fund. Partners who can make a substantial contribution to real estate objects to be digitized can register for a place in our consortium.
In the period 2019-2023, Block Materials participated in the European Digital Deconstruction project. The aim of the project was to implement new digital instruments for the demolition or dismantling of materials in buildings. With partners, Block Materials has succeeded in implementing the instruments 3D scan, Releasability, Digital Materials Database and Blockchain as Property Right. The last two instruments are made by Block Materials and were built within the Cirdax environment of sister company ReUseMaterials. Based on this infrastructure, Block Materials continues to build solutions for Circular Construction and Demolition in various regions in Europe.

Block Materials’ way of working has a robust basis in the scientific principles of Law and Economics. The application of Blockchain technology within this methodological framework ensures that every material in a building has a well-defined ownership right. This combination of real estate, property rights and new technology has been elaborated on for all facets of innovation related to the reuse of materials in the book Flexible Real Estate with Blockchain. You can download this book here.
Download our handbook English
